Kā vēlies turpināt?
Get in touch
In 1936, the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) issued the first international trade rules under the name Incoterms (International commerce terms). It is a set of rules that determines standardized conditions for the delivery of international cargo and ensures legal protection of international trade participants' transactions. International trade rules define cargo transportation tasks, risks and redistribution of cargo delivery related costs between the seller and the buyer.
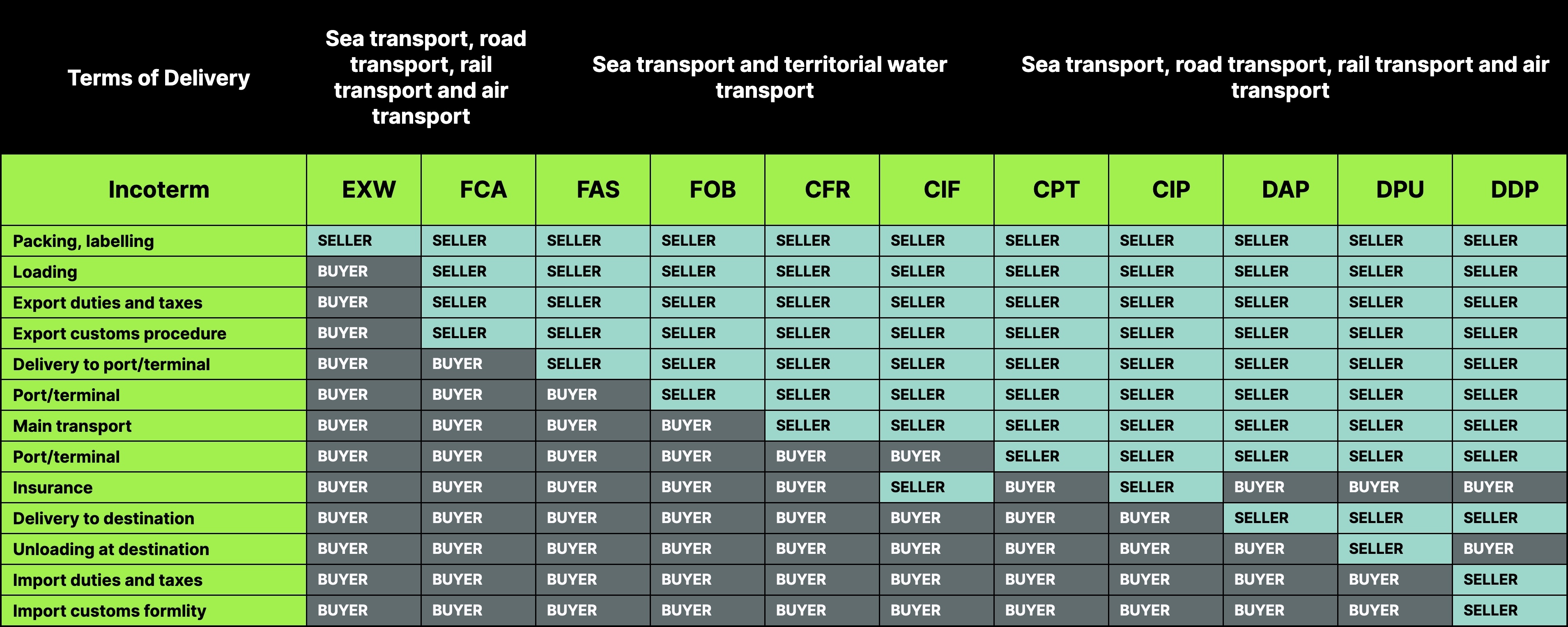
The Incoterms rules contain 11 terms that regulate the conditions of cargo transportation, risks and redistribution of delivery related costs between the seller and the buyer.
The 11 terms of the Incoterms delivery rules are divided into 4 groups. Each Incoterms rule is denoted by a three-letter abbreviation. The first letter in the name of the rule determines the moment of risk transfer from the seller to the buyer during further transportation:
In Incoterms rules, 7 out of 11 terms apply to transportation by all types of vehicles and 4 only to sea transport and territorial water transport.
|
EXW (Ex Works) |
EXW means that the seller ensures the availability of the goods to the buyer in its company's premises (factory, warehouse) and at a certain time. |
|
|
The buyer assumes all risks related to the transportation of the goods and all transportation related costs until the goods are delivered to their destination. |
|
|
According to this term, the buyer is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, as well as for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The EXW term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
The place of transfer of risks is the seller's premises. |
|
|
|
|
FCA (Free Carrier) |
The FCA terms provide that the seller is obliged to deliver the goods to the place of delivery agreed with the buyer. |
|
|
If the agreed place is the seller's factory or warehouse, it is the seller's responsibility to ensure that the goods are loaded into the buyer's vehicle. If the agreed place of delivery is another specified place, it is the responsibility of the seller to ensure the loading of the goods and their delivery to the agreed place of delivery. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The FCA term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
The risks are transferred depending on the place of delivery of the goods – at the seller's premises, or at the specified place where the goods are unloaded from the seller's vehicle. |
|
|
|
|
CPT (Carriage Paid To) |
The CPT terms provide that the seller and the buyer can agree that the destination of goods delivery can be any place on the way from the seller's premises to the place indicated by the buyer. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the entire transportation process to the destination of goods transfer specified by the buyer and covers all costs related to this stage. |
|
|
The CIP term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risks are transferred when the goods are accepted by the carrier hired by the buyer. |
|
|
|
|
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To) |
The CIP terms provide that the seller and the buyer can agree that the destination of goods delivery can be any place on the way from the seller's premises to the place indicated by the buyer. In addition, the seller must provide goods insurance for the entire stage of goods delivery. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the entire transportation process to the destination of goods transfer specified by the buyer and covers all costs related to this stage. |
|
|
The CIP term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risks are transferred when the goods are accepted by the carrier hired by the buyer. |
|
|
|
|
DAP (Delivered at Place) |
The DAP terms provide that the place of delivery of goods is the place specified by the buyer in the country of destination. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the entire transportation process to the destination of goods transfer specified by the buyer and covers all costs related to this stage. |
|
|
The DAP term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risk is transferred to the buyer at the moment when the goods have been delivered to the specified place and are ready for unloading. |
|
|
|
|
DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded) |
The DPU terms provide that the place of delivery of goods is the place specified by the buyer in the country of destination. According to the term, the goods are considered delivered when they are unloaded from the transport provided by the seller and handed over to the buyer. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the entire transportation process to the destination of goods transfer specified by the buyer and covers all costs related to this stage. |
|
|
The DPU term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risk is transferred to the buyer at the moment when the goods have been delivered to the specified place and unloaded from the transport. |
|
|
|
|
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) |
The DDP terms provide that the place of delivery of goods is the place specified by the buyer in the country of destination. According to the term, the goods are considered delivered when they are unloaded from the transport provided by the seller and handed over to the buyer. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the entire transportation process to the destination of goods transfer specified by the buyer and covers all costs related to this stage. |
|
|
The DDP term provides that both the buyer and the seller have access to all types of transport services – by sea, rail, road or air. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, as well as for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risk is transferred to the buyer at the moment when the goods have been delivered to the specified place and unloaded from the transport. |
|
|
|
|
FAS (Free Alongside Ship) |
The FAS term is the first Incoterm provision governing international maritime trade transactions. The FAS terms provide that the place of delivery of goods is the port terminal specified by the buyer. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the transport process up to the port terminal specified by the buyer for loading onto the ship and covers the costs related to this entire stage of transportation. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
Risks are transferred to the buyer at the moment of unloading the goods at the port terminal specified by the buyer and at the time of handing over the relevant documentation to the buyer. |
|
|
|
|
FOB (Free On Board) |
The FOB terms provide that the seller must deliver the goods to the vessel booked by the buyer at a specified place and time. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for ensuring the transport process until the goods are loaded on the ship and covers the costs related to this entire stage of transportation. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risks are transferred to the buyer when the goods are loaded on the ship. |
|
|
|
|
CFR (Cost and Freight) |
The CFR terms provide that the seller shall deliver the goods to the booked vessel at a specified place and time. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for packaging and labelling the goods, loading the goods for inland transport and unloading them on the cargo vessel pre-booked by this party and the costs associated with this entire stage of transportation including the cost of transportation to the port of destination. |
|
|
The buyer's obligations resume when the goods arrive at the port of destination. The buyer ensures the unloading of the goods from the ship, their further transportation, carrying out customs procedures and unloading of the goods at the destination of the shipment of the goods. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risks are transferred to the buyer when the goods are loaded on the ship. |
|
|
|
|
CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight) |
The CIF terms provide that the seller shall deliver the goods to the booked vessel at a specified place and time. In addition, the seller must provide goods insurance for the entire stage of goods delivery. |
|
|
The seller is responsible for packaging and labelling the goods, loading the goods for inland transport and unloading them on the cargo vessel pre-booked by this party and the costs associated with this entire stage of transportation including the cost of transportation to the port of destination and insurance. |
|
|
The buyer's obligations resume when the goods arrive at the port of destination. The buyer ensures the unloading of the goods from the ship, their further transportation, carrying out customs procedures and unloading of the goods at the destination of the shipment of the goods. |
|
|
According to this term, the seller is responsible for carrying out export customs procedures and paying taxes, and the buyer is responsible for carrying out import customs procedures and paying taxes. |
|
|
The risks are transferred to the buyer when the goods are loaded on the ship. |
Have questions? Get a consultation within 1 hour
Contact us in the most convenient way for you – remotely via WhatsApp / Zoom / phone / e-mail or in person